Representation & Narrative theory
Representation
The ideology of representation in media is one which is theorised by many philosophers as it is very important in todays society.
Stuart Hall's theory of encoding and decoding is an important part of audience theory and aids to help audience how an audience will think. This theory suggests that the director encodes a particular message or meaning which the audience can analyse and decode to find out the meaning. Hall believes decoding is the most important part of theory as not many theorists analyse it. We decode depending on psychographics and demographics personal to the viewer. Hall also believes that audience members adopt one of 3 opinions to what they are seeing:
- Dominant / Preferred reading - this is the opinion which the director wants the audience to take. This will likely be due to a similar age, culture or background which the audience member and director may share.
- Oppositional reading - this is an opposing opinion to which the director wants and is normally uncommon unless the media contains controversial topics
- Negotiated reading - where the audience accepts part of the directors views however disagrees with other views within the media text
Levi Strauss who was an anthropologist in the 1900's suggested a theory of 'binary opposites' which highlights that most narratives in film have opposing main characters in order to create contrast within the media text. For example, a strong male character and a damsel in distress is a binary opposition. This has become so common in films we don't recognise it anymore.
Roland Barthes' theory of semiotics reflects that our actions and thoughts are guided by many conventions and cultural background. Semiotics suggests that there are signs which signify a different meaning depending on who is interpreting them. Semiotics says that there are 3 types of signs:
Iconic signs - Icons are signs where meaning is based on similarity of appearance.
Indexical signs - Signs with a cause and effect relationship between the sign and its meaning.
Symbolic signs - Signs that have a conventional link.
Narrative
There are 4 narrative structures which are:
Linear structure - The narrative follows a clear beginning, middle and end which is very conventional. The ending will provide closure to the storyline.
Non linear structure - The narrative cuts from flashbacks to the future constantly making the movie loose its chronological order.
Open structure - Same as linear however the ending will be left open to interpretation which leaves the room for a sequel.
Circular structure - The film starts and ends with a climax which takes the audience to back where they started.
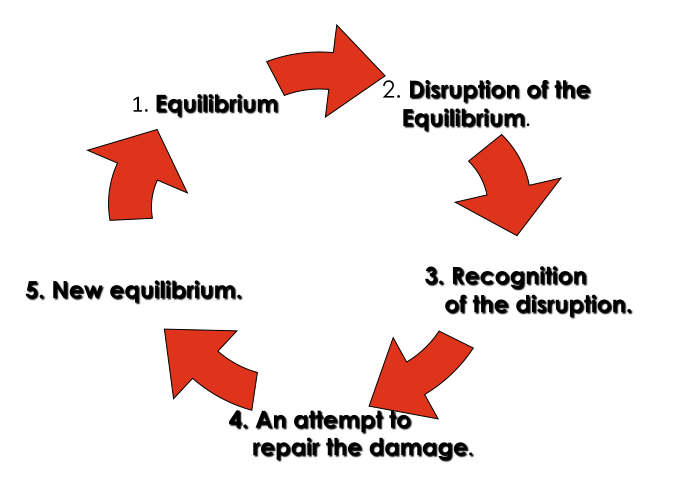
Narrative is a sequence of events that are combined in sequence to be presented to an audience. They can either be fictional or non-fictional. Todorov was a philosopher during the 20th century who theorised the idea of Equilibrium. The image below shows his theory of how a storyline works in a narrative.
However this theory does have its advantages and disadvantages. It is simple and easy to understand therefore making it very usable. On the other hand, nowadays the theory seems outdated and some films even try to ignore it in order to be seen as changing the understanding of narrative.

Comments
Post a Comment